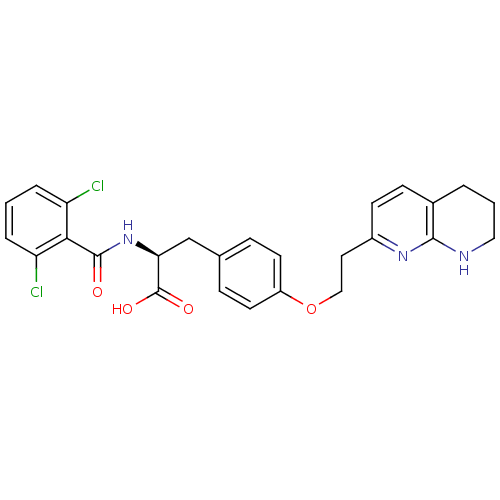
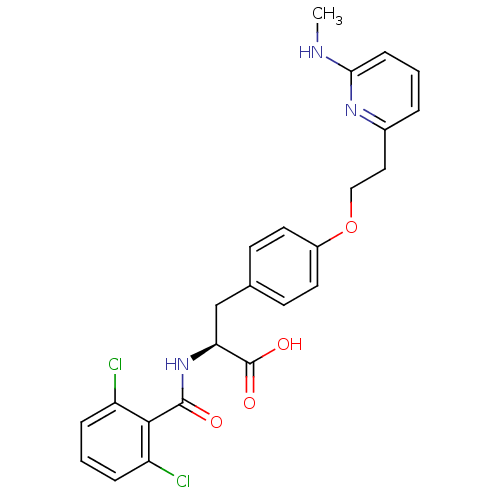
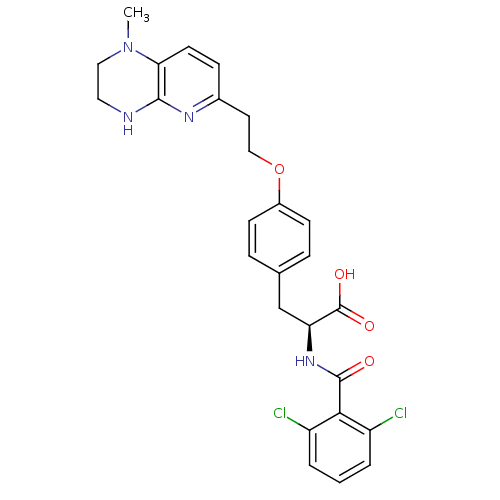
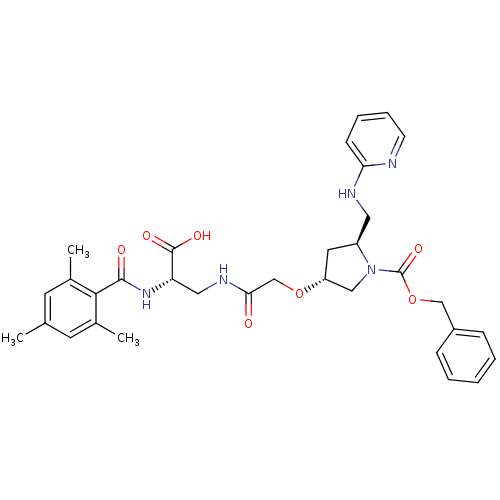
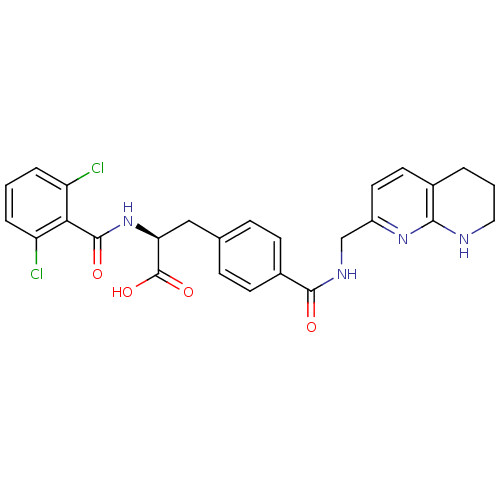
Affinity DataIC50: 2nMAssay Description:Antagonist activity at integrin alpha5beta1 in human A375M cells assessed as inhibition of cell adhesion to fibronectin in presence of Mg2+ and MK-04...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 97nMAssay Description:Antagonist activity at integrin alpha5beta1 in human A375M cells assessed as inhibition of cell adhesion to fibronectin in presence of Mg2+ and MK-04...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 130nMAssay Description:Antagonist activity at integrin alpha5beta1 in human A375M cells assessed as inhibition of cell adhesion to fibronectin in presence of Mg2+ and MK-04...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 150nMAssay Description:Antagonist activity at integrin alpha5beta1 in human A375M cells assessed as inhibition of cell adhesion to fibronectin in presence of Mg2+ and MK-04...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 200nMAssay Description:Antagonist activity at integrin alpha5beta1 in human A375M cells assessed as inhibition of cell adhesion to fibronectin in presence of Mg2+ and MK-04...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 210nMAssay Description:Antagonist activity at integrin alpha5beta1 in human A375M cells assessed as inhibition of cell adhesion to fibronectin in presence of Mg2+ and MK-04...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 610nMAssay Description:Antagonist activity at integrin alpha5beta1 in human A375M cells assessed as inhibition of cell adhesion to fibronectin in presence of Mg2+ and MK-04...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 1.40E+3nMAssay Description:Antagonist activity at integrin alpha5beta1 in human A375M cells assessed as inhibition of cell adhesion to fibronectin in presence of Mg2+ and MK-04...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 2.20E+3nMAssay Description:Antagonist activity at integrin alpha5beta1 in human A375M cells assessed as inhibition of cell adhesion to fibronectin in presence of Mg2+ and MK-04...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair